What is plantar fasciitis?
Plantar fasciitis is a common cause of heel pain, typically affecting the bottom of the foot. It occurs when a strong band of tissue, the plantar fascia, which runs along the sole of the foot, becomes inflamed, causing significant pain during walking or running.
Anatomy
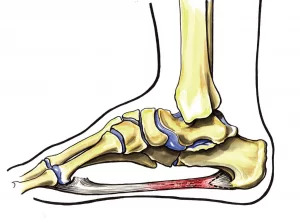
The plantar fascia is a ligament located just beneath the skin on the sole of the foot. It connects the heel bone to the toes and supports the arch of the foot.
What are the main causes?
The plantar fascia is designed to absorb shock and bear the loads placed on the feet. In many cases, the exact cause of plantar fasciitis is not clearly identifiable. However, excessive and repetitive stress can injure the fascia, causing small tears that result in pain and inflammation.
Risk factors that may contribute to plantar fasciitis:
- Limited ankle flexibility due to tight calf muscles
- Obesity
- Flat feet or high foot arches
- Certain athletic activities involving repetitive stress such as long-distance running, especially on hard surfaces like asphalt, as well as ballet and dance
- Poor running or walking technique that leads to uneven pressure on the foot and fascia
- Occupations that require prolonged standing or walking
Get the Help You Need Today!
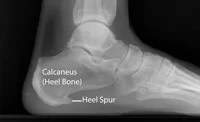
Heel Spur
Although many people with plantar fasciitis also have a heel spur, the spur itself does not cause the condition. Only about 5% of people with a heel spur go on to develop plantar fasciitis.
Plantar Fasciitis: What are the symptoms?
The most common symptom is pain on the plantar surface of the heel. The pain is often worse in the morning after getting out of bed or after long periods of rest, but it usually improves gradually with walking.
How is it diagnosed?
Diagnosis is made through patient history and clinical examination. There is usually tenderness at the base of the heel.
X-rays can help rule out other causes of pain. In persistent cases that do not improve with standard treatment, an MRI may be considered.
What does treatment for plantar fasciitis include?
Conservative Treatment
Treating plantar fasciitis can be a slow process that requires patience and consistency. Conservative management includes:
Stretching: Stretching the plantar fascia and the muscles at the back of the leg is essential and effective in reducing pain and preventing recurrence.
Rest: Reducing or stopping the activity that caused the inflammation may be necessary. Switching to a non-impact sport like swimming can help maintain fitness and aerobic conditioning.
Ice therapy: Applying ice 3–4 times daily for 15–20 minutes can reduce inflammation. This can be combined with gentle massage on the sole.
Biological Therapies
In persistent cases, an injection of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) may help regenerate the damaged fascia and speed up healing by leveraging the body’s own natural healing properties, without chemical substances.
Cortisone Injections
In very painful cases that do not respond to typical conservative treatment, a local cortisone injection may be administered. Cortisone is a powerful anti-inflammatory agent that can reduce inflammation and pain. However, multiple injections should be avoided as they can increase the risk of fascia rupture.
Physiotherapy
Various physiotherapy techniques can help reduce inflammation and promote faster recovery.
Get the Help You Need Today!
Surgical Treatment
Surgery for plantar fasciitis is extremely rare and is only considered after at least 12 months of systematic conservative treatment with no improvement.
Plantar Fascia Release: For patients who have normal ankle range of motion but persistent plantar fascia symptoms, partial release of the fascia may be considered.
Gastrocnemius Lengthening: This procedure is reserved for cases where calf muscles remain tight despite consistent stretching and prevent proper dorsiflexion of the foot. Tight calf muscles can lead to increased tension on the plantar fascia.
This surgery is done using minimally invasive methods with very small incisions.
