What is the anatomy of the ankle joint?
The ankle joint is formed by the articulation of three bones: the distal end of the tibia, the fibula, and the talus. These three bones are held together by a network of ligaments, which stabilize the joint and protect it from abnormal movements and injuries.
Articular cartilage is the smooth, white, and soft tissue that covers the joint surfaces of the bones, allowing them to glide against each other and facilitating smooth motion while also absorbing shock. This is a specialized type of cartilage known as hyaline cartilage.
What are chondral injuries?
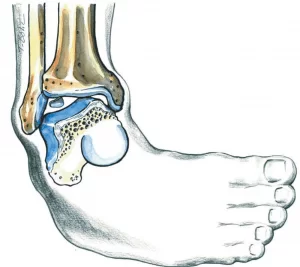
The articular cartilage can be damaged due to trauma—such as a sprain—or through gradual wear and tear. Chondral injuries are often the result of sports-related trauma, which may cause compression or detachment of a portion of the articular cartilage.
Get the Help You Need Today!
What are the symptoms of chondral injuries?
When cartilage is damaged, the joint can no longer function smoothly. This can lead to:
- Premature arthritis, which may result in full joint degeneration
- Pain
- Joint effusion (swelling due to excess synovial fluid)
- Mechanical symptoms such as joint locking or clicking caused by a loose fragment
How are chondral injuries diagnosed?
Diagnosis is made through a combination of:
- Medical history
- Symptoms
- Clinical examination
- Imaging tests such as X-rays and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
What is the appropriate treatment for chondral injuries?
Since articular cartilage lacks its own blood supply, the body cannot heal it naturally with new hyaline cartilage. Modern medicine has developed various techniques to assist in the regeneration of cartilage and to slow the progression of possible arthritis.
New biological treatments, such as injections of:
- Stem cells or autologous chondrocytes
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP)
…either alone or in combination with arthroscopy, can significantly help restore the cartilage and allow the patient to return to pre-injury activity levels.
Ankle Arthroscopy
Ankle arthroscopy is a minimally invasive technique involving two small incisions through which the surgeon can:
- Remove loose cartilage fragments
- Debride (clean) the damaged area and perform microfractures
- Transplant autologous chondrocytes
- Transplant osteochondral autografts (cartilage and bone cylinders from non-weight-bearing areas of the joint) to restore the defect
Get the Help You Need Today!
What should be considered during rehabilitation?
An effective rehabilitation program is essential and should include:
- Physiotherapy
- Kinesiotherapy
- Strengthening exercises
- Proprioceptive training
These components are vital to ensure a safe and complete return to previous activity levels.
