Non-Surgical Therapy for Orthopedic Conditions and Sports Injuries Promises Hope
What is the use of stem cells in medicine?
In recent years, stem cells have been widely used in medicine for various therapeutic purposes, such as in cases of hematologic diseases (e.g., leukemia), rheumatoid arthritis, as well as for wound and burn healing. Most widely known to the public are the stem cells collected from the umbilical cord at birth, which can be stored for potential future tissue regeneration.
Today, stem cells in orthopedics are creating new possibilities in the treatment of orthopedic conditions and sports injuries due to their regenerative capabilities. The method is already well established abroad, with famous athletes like basketball player Kobe Bryant and tennis player Rafael Nadal choosing this treatment and significantly reducing their recovery time after injuries.
The use of stem cells in orthopedics is considered safe and without complications, mainly because it involves autologous tissue — cells derived from the patient’s own body.
What are stem cells?
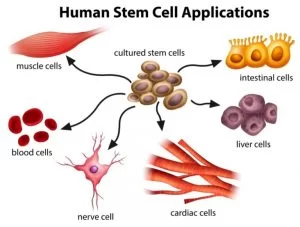
Stem cells are essentially undifferentiated cells that have the ability to differentiate into various tissue cells of the body. In the right environment, they can develop into heart, liver, bone, nerve, cartilage, tendon, ligament cells, and more. They are the foundational cells from which all the cells of our body’s organs originate.
Get the Help You Need Today!
What are the types of stem cells?
There are two main categories of stem cells:
- a) Embryonic stem cells
- b) Adult stem cells
Orthopedic surgery focuses on adult mesenchymal stem cells, which are found in the bone marrow and adipose tissue of fully developed organisms. When placed in the appropriate environment, adult stem cells can generate specific tissues such as bone, cartilage, muscle, and others.
When is stem cell therapy recommended in Orthopedics?
Stem cell therapy in orthopedics can be used in conditions where tissue structure is damaged, aiming to regenerate healthy tissue and replace the damaged part.
Specifically, stem cells can be used to treat the following:
- Cartilage tears and cartilage damage
- Tendonitis and tendinopathies
- Partial tears of shoulder tendons
- Early or advanced arthritis in any joint
- Muscle tears and strains
- Partial tears of the anterior or posterior cruciate ligament in the knee
- Partial meniscus tears
- Avascular necrosis of the femoral head in the hip (early stages)
- Arthritic changes in the spine
- Partial tear of the Achilles or other tendons
Get the Help You Need Today!
What are the main advantages of stem cell therapy?
- Safe and painless method (since it uses biological material from the patient’s own body)
- Faster regeneration of injured tissue
- Quicker recovery of mobility
- Faster return to daily activities and sports, without scars or visible marks
- Significant pain reduction
- In many cases, it helps avoid surgery altogether
What is the procedure for stem cell treatment?
Stem cells are collected from either adipose tissue (fat) or bone marrow. Both collection methods are equally effective.
The procedure takes place in a hospital under sterile conditions and is relatively simple. Specialized laboratories in Greece then handle the cultivation and differentiation of the stem cells.
From adipose tissue
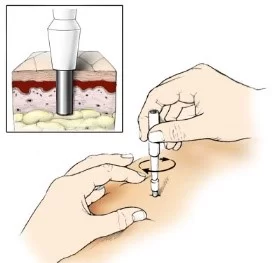
Local anesthesia is applied, and a small incision is made to collect a small amount of adipose tissue, usually from the abdomen, or near the affected area if combined with a surgical procedure (e.g., arthroscopy).
The tissue is then sent to a lab, where the stem cells are isolated and cultured. The cultured stem cells are then activated to begin differentiation into the type of tissue that has been damaged. These cells are then injected into the affected area by the orthopedic specialist under sterile conditions.
From bone marrow

A small amount of bone marrow is aspirated from the iliac crest of the pelvis and centrifuged to separate stem cells from other components. Because the final concentrated solution contains a high number of stem cells and growth factors, culturing is not necessary. This simplifies the process, allowing the stem cells to be injected directly into the affected area.
Stem cell therapy in Orthopedics is performed by experienced and specialized physicians following specific medical protocols for harvesting, preparation, and application.
Usually, the treatment is completed with personalized physiotherapy programs to achieve even better results.
